FSHM Weekly-09/06/2024 Hands-on Session in Shell-Scripting
Blog of shell scripting session at Maitri


In this session we have learned the basic shell scripting with hands on coding using Bash shell. Below are the brief explanation of this session topic with its related things.
What is Shell Scripting?
In simple terms it is a series of shell cmds or linux cmds that is used for automation, it is a scripting language and also known as interpreted language where each code is executed line by line. it has a simple syntax that can be easily learned and it is used for small task and not for complex task.
Linux architecture
Components
- Hardware - computing resources, GPU, RAM, CPU etc..
- Kernel - heart of your linux which is the main component for the user interface between hardware and software
- Shell - For running cmds to directly communicate with kernel
- Application - Top layer like browsers..
Shell:
GNU Bourne-Again Shell (bash) is the most popular and default shell used in many linux distros.
When you start the bash shell .bashrc or .bash_profile it used as a startup script which allows to customize the the behavior of the shell.
$ – When a shell is used interactively, it displays a $ when it is waiting for a command from the user. This is called the shell prompt.
# – When shell is running as root, this is called super user shell prompt.
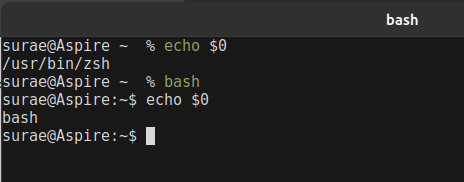
First Bash script:
Bash script files has the extension of .sh, however it can run without sh perfectly fine
We will be using Vim editor or Vi editor for creating for simple first shell script you can use any editors.
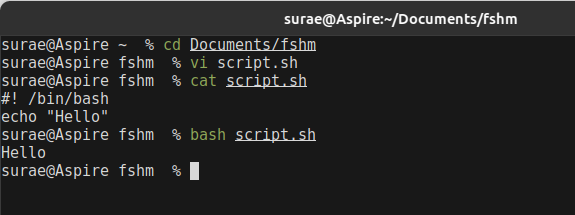
- In the above #! /bin/bash this is the first line of script for mentioning our default shell this is also called as shebang.
- echo cmd it is used to print or display text or string
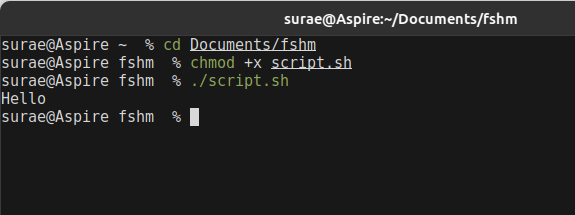
- For execution there are two ways:
- whether you can give bash command and script name
- With Another thing by giving permission for execution as shown below..
Basic Linux Cmds:
| CMDS | Discription |
|---|---|
| mkdir [directory_name] | Create a new directory. |
| rm [file_name] | Remove a file. |
| rm -r [directory_name] | Remove a directory recursively. |
| rm -rf [directory_name] | Recursively remove a directory without requiring confirmation. |
| cp [source_file] [destination_file] | Copy the contents of one file to another file. |
| cp -r [source_directory] [destination_directory] | Recursively copy a directory to a second directory. |
| mv [source_file] [destination_file] | Move or rename files or directories. |
| ln -s [path]/[file_name] [link_name] | Create a symbolic link to a file. |
| touch [file_name] | Create a new file. |
| cat [file_name] | Show the contents of a file. |
| cd cd ~ | Change directory to $HOME. |
| pwd | Show the directory you are currently working in. |
| cd [directory_path] | Change location to a specified directory. |
Directory navigation with scripts:
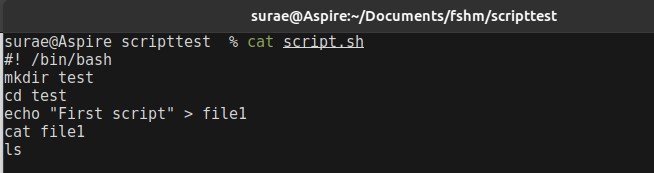
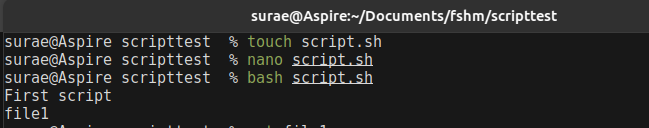
By using above linux cmd lets create a directory with a simple file with a content, this all can be done by running a single script. In the below script we have made a new directory using mkdir and cd for going into that directory and by using echo we can write content into file then cat to read or show the content then ls for listing the directory.
Arithmetic Expressions:
| Operator | Usage |
|---|---|
| + | addition |
| - | subtraction |
| * | multiplication |
| / | division |
| ** | exponentiation |
| % | modulus |
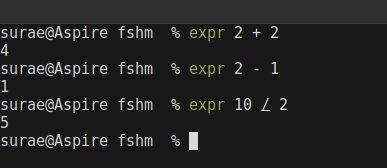
Above are the operators supported by bash for mathematical calculations.
Numerical expressions can also be calculated and stored in a variable using the syntax below:
var=$((expression))
Let's try an example.
#!/bin/bash
var=$((3+9))
echo $var
Fractions are not correctly calculated using the above methods and truncated.
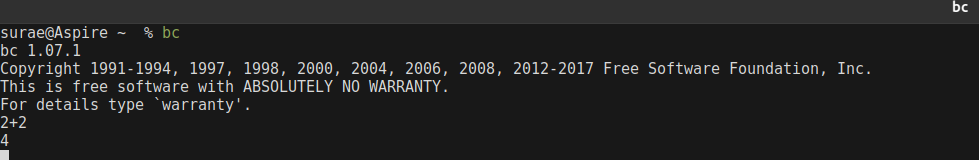
For decimal calculations, we can use bc command to get the output to a particular number of decimal places. bc (Bash Calculator) is a command line calculator that supports calculation up to a certain number of decimal points.
echo "scale=3;25/7" | bc
Where scale defines the number of decimal places required in the output.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Enter a numner"
read a
echo "Enter a numner"
read b
var=$((a+b))
echo $var
In bash, we can take user input using the read command.
read -p "Enter your age" variable_name
Comparison is used to check if statements evaluate to true or false. We can use the below shown operators to compare two statements:
| Operation | Syntax | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Equality | num1 -eq num2 | is num1 equal to num2 |
| Greater than equal to | num1 -ge num2 | is num1 greater than equal to num2 |
| Greater than | num1 -gt num2 | is num1 greater than num2 |
| Less than equal to | num1 -le num2 | is num1 less than equal to num2 |
| Less than | num1 -lt num2 | is num1 less than num2 |
| Not Equal to | num1 -ne num2 | is num1 not equal to num2 |
Some Example scripts :
- Script for checking if a service is running and restarts it if it is not.
#!/bin/bash
# Service name
SERVICE_NAME="docker"
# Check if the service is running
if ! systemctl is-active --quiet "$SERVICE_NAME"; then
# Restart the service
systemctl restart "$SERVICE_NAME"
echo "$SERVICE_NAME restarted!"
else
echo "$SERVICE_NAME is running."
fi
- Database Backup Script – It creates a backup of a MySQL database and stores it in a specified directory.
#!/bin/bash
# Database credentials
DB_USER="your_db_user"
DB_PASSWORD="your_db_password"
DB_NAME="your_db_name"
BACKUP_DIR="/path/to/backup"
# Create a timestamp
TIMESTAMP=$(date +"%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
# Create a backup
mysqldump -u "$DB_USER" -p"$DB_PASSWORD" "$DB_NAME" > "$BACKUP_DIR/db_backup_$TIMESTAMP.sql"
echo "Database backup completed successfully!"- Script to check are we in the python environment or not.
#!/bin/bash
if [[ -n "$VIRTUAL_ENV" ]]; then
echo "You are in a virtual environment: $VIRTUAL_ENV"
else
echo "You are NOT in a virtual environment"
fiCredits to the speaker of this session Jagadesh, who is an Foss enthusistic working in an mnc, Thanks Jagadesh and Thanks to FSHM for conducting this kind of sessions.
